Dealing with physical pain is always frustrating, especially when it affects our mobility, which is certainly the case when it comes to hip bursitis.
Small sacs of a lubricant-like fluid called bursa are located throughout the body, in joints like the shoulder, elbow, knee, and hip. The bursa provides a cushion and reduces friction, between bones and surrounding soft tissue in our joints.
Any issues with the bursa, such as inflammation, can cause moderate to severe pain and make day-to-day activities difficult.
This condition is not the same thing as hip tendonitis, although both issues can cause painful hip symptoms.
What is Bursitis of the Hip?
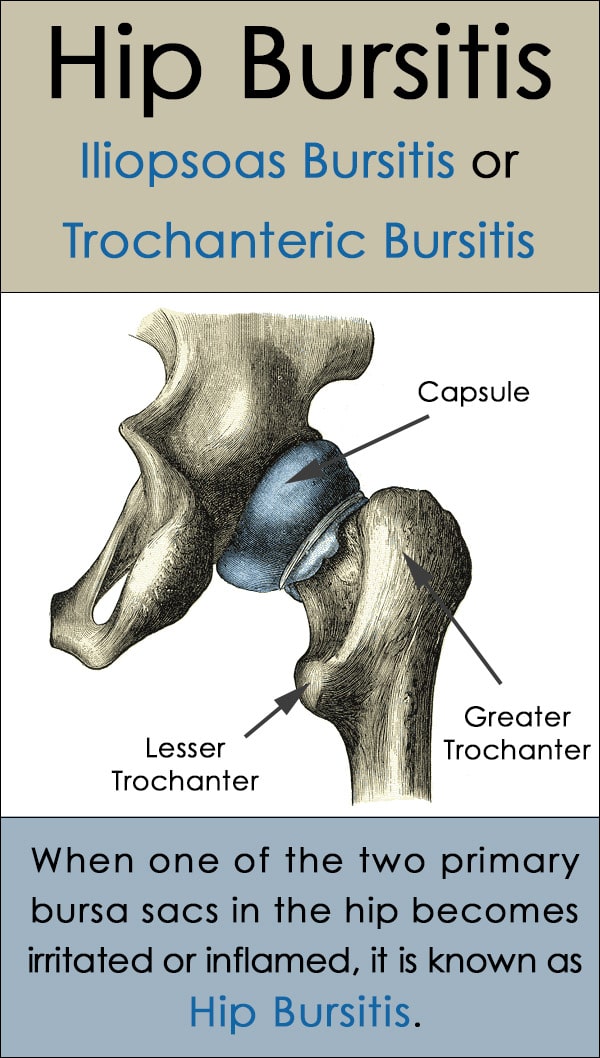
When one of the two primary bursa sacs in the hip becomes irritated or inflamed, the condition is known as bursitis of the hip.
The bursa sac located in the outer or bony side of the hip, an area called the greater trochanter, is where most people experience hip bursitis. This is sometimes referred to as trochanteric bursitis.
Trochanteric bursitis symptoms are fairly common, affecting an estimated 15 percent of women and 8 percent of men.
Iliopsoas bursitis occurs when the bursa sac located on the groin side of the hip becomes inflamed or irritated. Here, the pain associated with bursitis is felt on the inner side of the hip. This form of hip bursitis is less common.
The treatment for hip bursitis, however, is similar regardless of whether it’s iliopsoas or trochanteric bursitis.
What Are the Causes of Hip Bursitis?
The causes of hip bursitis to flare up can vary from person to person. Unfortunately, normal wear and tear on the hip that comes with the aging process can lead to the condition. That said, anyone can suffer from bursitis of the hip for a number of different reasons.
Some common causes of hip bursitis can include:
- Overuse injuries or repetitive stress can be a big factor, especially for athletes with sustained training regimens or in others with occupations that require standing or strenuous activity for extended periods of time.
- Bone spurs are tiny projections that can develop along the edges of bone, including the greater trochanter. These projections can rub up against the bursa and cause swelling or irritation.
- Trauma or injury can cause bursitis in the hip. These are incidents like a fall, a hard bump, or other types of impacts to the hip. Even long periods of lying on one side of the body, such as in recovery from surgery or another injury, can cause the condition.
- Different leg lengths, which cause a person’s weight to fall to one side, may play a factor.
- Other health issues, such as rheumatoid arthritis, spine disease (scoliosis), or past surgeries near the hip, can lead to an inflamed or sensitive bursa.
What Are Common Hip Bursitis Symptoms?
Generally, people suffering from hip bursitis experience pain at the hip. This can then spread to the thigh area. If they’re suffering iliopsoas bursitis symptoms, the pain occurs on the inside or the groin side of the hip.
More specific hip bursitis symptoms can include:
- Sharp or intense pain in the hip
- Stiffness or achiness in the area that begins to spread across the hip region
- Sensitive to the touch or pain when moving the joint
Many people experience painful symptoms at night, especially when they’re laying on the irritated hip. Standing after being seated for a long time can also cause pain to resonate. Physical activities, like walking, hiking, running, or squatting during a flare up of hip bursitis can make the pain more intense.
Understanding the symptoms of this condition is important so that a person knows what movements or positions to avoid, if possible, or when to seek treatment for hip bursitis.
Hip Bursitis Treatment
A diagnosis of hip bursitis will involve a physical examination, a discussion of symptoms and, in some cases, a physician will order X-rays or an MRI in order to rule out any other conditions that may be causing hip pain.
There is a range of approaches for hip bursitis treatment. These can include some of the following:
1. Rest
Both rest and avoiding activities that cause pain can allow time for the inflammation in the hip bursa to subside. If complete rest is not possible, keep any strenuous movements to a minimum as much as possible.
2. Crutches or Cane For Support
Using crutches or a cane for support during a hip bursitis flare is a recommended method for providing support, and giving the tender hip joint time to heal. Crutches will work best, although a cane or sturdy walking stick will reduce some stress on the hip.
3. Pain Medications
Nonsteroidal, anti-inflammatory pain medications like ibuprofen (Advil, Motrin) or naproxen (Aleve) are useful in reducing pain and inflammation. These can be purchased without a prescription at any pharmacy and are generally safe to use daily during recovery.
4. Physical Therapy
Physical Therapy is a good option for learning hip bursitis exercises. These are stretches and movements to increase flexibility and strength. After learning the most effective ones with just a few sessions, these exercises can be performed at home.
Specialized physical therapy for athletes or occupational workers may also include learning the proper form of a particular movement in order to avoid further injury and prevent new ones in the future.

5. EPAT Therapy
EPAT Therapy, sometimes referred to as Extracorporeal Shock Wave Therapy (ESWT), is a noninvasive method for speeding up healing and bursitis-related downtime.
EPAT is a painless treatment that delivers impulse pressure waves deep into the soft tissue surrounding the bursa. These “shockwaves” increase blood flow and decrease inflammation and pain to the affected area of the hip.
Because there are no side effects, anesthesia, or infection risks with this non-surgical procedure, it is a useful approach for treating hip bursitis while maintaining the ability to work or, in the case of athletes, sometimes continue to train and perform throughout recovery.
6. Cortisone Steroid Injections
Steroid Injections of Cortisone directly into the bursa can relieve pain and inflammation. Corticosteroids are powerful anti-inflammatories and an injection may provide temporary or prolonged relief.
Depending on the severity of the injury, a person might need another injection after several months. However, too many steroid injections can damage the surrounding soft tissue and lead to weakness and further issues.
7. Surgery (Bursectomy)
In the most serious cases, when all other treatment approaches have failed, surgery to remove the bursa sac can be performed. This type of surgery is known as a Bursectomy and the hip is able to function normally without the bursa sac.
However, this option might not be appropriate for middle aged to younger, high-performing athletes or workers.
A bursectomy procedure is generally done in an outpatient setting and will require a period of rehabilitation. As with all surgeries, there is a risk of complications and all treatment options should be thoroughly discussed with your physician.
Any form of pain or injury can prohibit regular movement or daily life activities, so it’s always important to speak with a physician or trainer at the first sign of an issue.
The hip bursitis treatment methods listed here have shown to be effective for speeding up the healing process and will often lead to a faster recovery by reducing inflammation and stress on the hip.